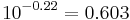Zeta Reticuli
|
Zeta Reticuli A and B. |
|
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 |
|
|---|---|
| Constellation | Reticulum |
| Zeta1 Reticuli | |
| Right ascension | 03h 17m 46.16324s[1] |
| Declination | −62° 34′ 31.1563″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.54 |
| Zeta2 Reticuli | |
| Right ascension | 03h 18m 12.81853s[1] |
| Declination | −62° 30′ 22.9048″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 5.24 |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | G3-5V / G2V[2] |
| U−B color index | 0.07 / 0.01 |
| B−V color index | 0.64 / 0.60[2] |
| R−I color index | 0.34 / 0.34[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +12.2 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 1,337.57[1] mas/yr Dec.: 649.12[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 83.28 ± 0.20[1] mas |
| Distance | 39.16 ± 0.09 ly (12.01 ± 0.03 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 5.12 / 4.83 |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 1,330.74[1] mas/yr Dec.: 647.11[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 83.11 ± 0.19[1] mas |
| Distance | 39.24 ± 0.09 ly (12.03 ± 0.03 pc) |
| Details | |
| Zeta1 Reticuli | |
| Mass | 0.958[3] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.84[4] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.54 ± 0.02[2] |
| Temperature | 5,746 ± 27[2] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | -0.22[2] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 1.98[5] km/s |
| Age | 1.5–3.0[6] Gyr |
| Zeta2 Reticuli | |
| Mass | 0.985[3] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.88[4] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.46 ± 0.01[2] |
| Temperature | 5,859 ± 27[2] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 1.74[5] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Zeta Reticuli (ζ Ret, ζ Reticuli) is a binary star system located about 39 light-years (12 pc) away from Earth. It is located in the constellation Reticulum, and is visible to the unaided eye in very dark skies. Because of the southerly location of the system, it is not visible north of the tropics.
Contents |
Characteristics
As a declination of −62°, the system is not visible from Britain's latitude of +53°, so it never received a Flamsteed designation in John Flamsteed's 1712 Historia Coelestis Britannica. The Bayer designation for this star system, Zeta Reticuli, originated in a 1756 star map by the French astronomer Abbé Nicolas Louis de Lacaille.[7] Subsequently, the two stars received separate designations in the Cape Photographic Durchmusterung, which was processed between 1859 and 1903, then in the Henry Draper Catalogue, published between 1918 and 1924.[8]
The two stars are located at similar distances from the Sun and share the same motion through space,[9] confirming that they are gravitationally bound and form a wide binary star system. They have an angular separation of 309.2 arc seconds (5.2 arc minutes);[10] far enough apart to appear as a close pair of separate stars to the naked eye under suitable viewing conditions. The distance between the two stars is at least 3,750 AU, so their orbital period is 170,000 years or more.[11]
Both stars share similar physical characteristics to the Sun,[9] so they they are considered solar analogs. Their stellar classification is nearly identical to that of the Sun. ζ1 has 96% of the Sun's mass and 84% of the Sun's radius. ζ2 is slightly larger and more luminous than ζ1, with 99% of the Sun's mass and 88% of the Sun's radius.[3][4] The two stars are somewhat deficient in metals, having only 60% of the proportion of elements other than hydrogen and helium as compared to the Sun.[2][12] For reasons that remain uncertain, they have an anomalously low abundance of beryllium.[5] Both stars are considered unusual because they have a lower luminosity than is normal for main sequence stars of their age and surface temperature. That is, they lie below the main sequence curve on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram for newly formed stars. Most stars will evolve above this curve as they age.[10]
ζ1 has an intermediate level of magnetic activity in its chromosphere.[13] Although the kinematics of this system suggest that they belong to a population of older stars, the properties of their stellar chromospheres suggests that they are only about 2 billion years old.[14]
On September 20, 1996, a tentative discovery of a hot Jupiter around ζ2 was reported, but the discovery was quickly retracted as the signal was shown to be caused by pulsations of the star.[15] In 2002, ζ1 was examined at an infrared wavelength of 25 μm, but no indication of an excess of infrared radiation was found.[16] In 2007, the Spitzer Space Telescope was used to find an infrared excess at a wavelength of 70 μm around ζ2. This radiation is likely being emitted by a debris disk with a mean temperature of 150 K (−123 °C) that is orbiting the host star at a distance of 4.3 AU.[17] In 2010, the Herschel Space Observatory, looking for debris disks analogous to the Kuiper belt, around sun like stars, detected signs of a possible exo-kuiper belt, with a semi-major axis of 100 AU around ζ2.[18]
This star system belongs to the Zeta Herculis Moving Group of stars that have a common motion through space, suggesting that they share a common origin. The [U, V, W] components of the space velocity for this system are equal to [−70.2, −47.4, +16.4] km/s for ζ1 and [−69.7, −46.4, +16.8] km/s for ζ2.[2] They are presently following an orbit through the Milky Way galaxy that has an eccentricity of 0.24. This orbit will carry the system as close as 17.4 kly (5.33 kpc) and as far as 28.6 kly (8.77 kpc) from the galactic core. The inclination of this orbit will carry the stars as much as 1.3 kly (0.4 kpc) from the plane of the galactic disk.[19] This likely puts them outside the thick disk population of stars.[20]
See also
- Zeta Reticuli in fiction
- Role of Zeta reticuli in the story of the purported Betty and Barney Hill abduction by space aliens (Greys)
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664, Bibcode 2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j del Peloso, E. F.; da Silva, L.; Porto de Mello, G. F. (June 2000). "zeta1 and zeta2 Reticuli and the existence of the zeta Herculis group". Astronomy and Astrophysics 358: 233–241. Bibcode 2000A&A...358..233D.
- ^ a b c Takeda, G. et al. (2007). "Stellar parameters of nearby cool stars. II. Physical properties of ~1000 cool stars from the SPOCS catalog". Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 168: 297–318. Bibcode 2008yCat..21680297T. Note: see VizieR catalogue J/ApJS/168/297.
- ^ a b c Pasinetti Fracassini, L. E. et al. (February 2001). "Catalogue of Apparent Diameters and Absolute Radii of Stars (CADARS) - Third edition - Comments and statistics". Astronomy and Astrophysics 367 (2): 521–524. arXiv:astro-ph/0012289. Bibcode 2001A&A...367..521P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20000451. Note: using the method of Perrin and Karoji (1987).
- ^ a b c Santos, N. C. et al. (October 2004). "Beryllium anomalies in solar-type field stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 425 (3): 1013–1027. arXiv:astro-ph/0408109. Bibcode 2004A&A...425.1013S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20040510.
- ^ Mamajek, Eric E.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (November 2008). "Improved Age Estimation for Solar-Type Dwarfs Using Activity-Rotation Diagnostics". The Astrophysical Journal 687 (2): 1264–1293. Bibcode 2008ApJ...687.1264M. doi:10.1086/591785.
- ^ Ridpath, Ian (1989), Star tales, James Clarke & Co., p. 11, ISBN 0718826957, http://books.google.com/books?id=gFrdcTdeVaEC
- ^ Naming astronomical objects, International Astronomical Union, http://www.iau.org/public/naming/#stars, retrieved 2011-12-16
- ^ a b da Silva, L.; Foy, R. (May 1987). "Zeta-1 and Zeta-2 RETICULI - A puzzling solar-type twin system". Astronomy and Astrophysics 177 (1-2): 204–216. Bibcode 1987A&A...177..204D.
- ^ a b Makarov, V. V.; Zacharias, N.; Hennessy, G. S. (November 2008). "Common Proper Motion Companions to Nearby Stars: Ages and Evolution". The Astrophysical Journal 687 (1): 566–578. Bibcode 2008ApJ...687..566M. doi:10.1086/591638.
- ^ Kaler, James B., "ZETA RET (Zeta Reticuli)", Stars (University of Illinois), http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/zetaret.html, retrieved 2011-11-16
- ^ A metallicity of -0.22 indicates that they have the following proportion of metals compared to the Sun:
- ^ Vieytes, M.; Mauas, P.; Cincunegui, C. (October 2005). "Chromospheric models of solar analogues with different activity levels". Astronomy and Astrophysics 441 (2): 701–709. Bibcode 2005A&A...441..701V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20052651.
- ^ Rocha-Pinto, Helio J.; Maciel, Walter J.; Castilho, Bruno V. (March 2002). "Chromospherically young, kinematically old stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 384 (3): 912–924. arXiv:astro-ph/0112452. Bibcode 2002A&A...384..912R. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20011815.
- ^ "Life on Zeta Reticuli?". ZetaTalk. http://www.zetatalk.com/usenet/use90200.htm. Retrieved 2010-02-10.
- ^ Laureijs, R. J. et al. (May 2002). "A 25 micron search for Vega-like disks around main-sequence stars with ISO". Astronomy and Astrophysics 387 (1): 285–293. Bibcode 2002A&A...387..285L. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020366.
- ^ Trilling, D. E. et al. (February 2008). "Debris Disks around Sun-like Stars". The Astrophysical Journal 674 (2): 1086–1105. Bibcode 2008ApJ...674.1086T. doi:10.1086/525514. See table 6.
- ^ Eiroa, C. et al. (July 2010). "Cold DUst around NEarby Stars (DUNES). First results. A resolved exo-Kuiper belt around the solar-like star ζ2 Ret". Astronomy and Astrophysics 518. Bibcode 2010A&A...518L.131E. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014594.
- ^ Holmberg, J.; Nordström, B.; Andersen, J. (July 2009). "The Geneva-Copenhagen survey of the solar neighbourhood. III. Improved distances, ages, and kinematics". Astronomy and Astrophysics 501 (3): 941–947. Bibcode 2009A&A...501..941H. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200811191.
- ^ Makarov, V. V.; Zacharias, N.; Hennessy, G. S. (November 2008). "Common Proper Motion Companions to Nearby Stars: Ages and Evolution". The Astrophysical Journal 687 (1): 566–578. Bibcode 2008ApJ...687..566M. doi:10.1086/591638.
External links
- "Zeta Reticuli". SolStation. http://www.solstation.com/stars2/zeta-ret.htm. Retrieved 2008-08-31.
- "Zeta(1) Reticuli". The Internet Stellar Database. http://www.stellar-database.com/Scripts/search_star.exe?ID=23900. Retrieved 2008-08-31.
- "Zeta(2) Reticuli". The Internet Stellar Database. http://www.stellar-database.com/Scripts/search_star.exe?ID=24100. Retrieved 2008-08-31.
- "Zeta(3) Reticuli". Hatirla Beni Belgesel. http://hatirlabeni.net/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=401:zeta-reticulideki-uzayllar&catid=25:proje&Itemid=53. Retrieved 2008-08-31.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||